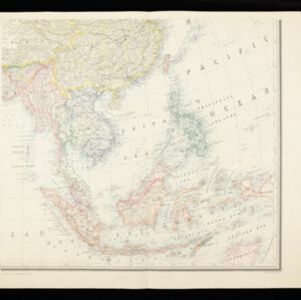
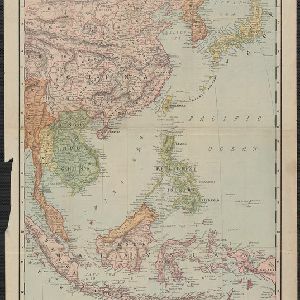
Map of Asia: Printed for the New York Central's 'Four-Track Series'
1900
Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Singapore, Brunei, Laos, Southeast Asia
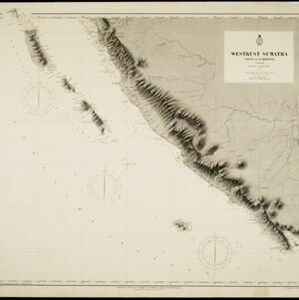
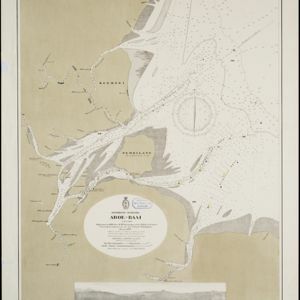
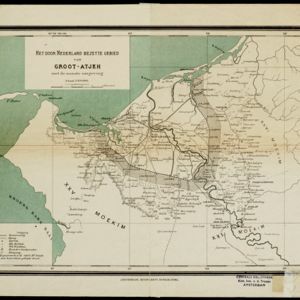
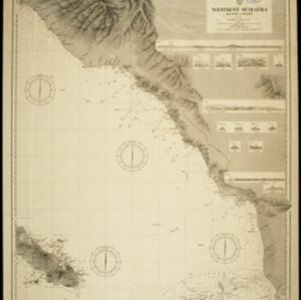
Colonial territory is labelled and colour-coded on this map of Southeast Asia. A list on the left edge gives the colonial status, size and population of Asian countries, and ranks the main cities by population. Gold and iron mines are marked.